Worm Gear Design Calculation Pdf Writer
This paper presents a numerical model to predict the wear of worm gear. This last is based on well-known Archard’s wear formulation. The influence of lubrication is taken into account with a local wear coefficient, depending on the ratio between the minimum lubricant film thickness and the amplitude of the surface roughness. When material on a wheel flank is worn, it is then necessary to update the surface profile, consequently the contact pressure calculations. To compute the quasi-static load sharing and thus the contact pressures required for the wear model, the equation of displacement compatibility is solved, using the influence coefficient method, which allows a fast and accurate computing. The bending deflections of the worm and wheel, and the local contact deformations of mating surfaces are included.
Worm Gear Efficiency Calculation
ModelEngineersUtilities: Model Engineers' Utilities is a useful suite of calculators for machinists This paper presents a physically grounded calculation method to determine the efficiency of worm gear drives. Design for safety coefficients entered. Free download worm gear design calculation pdf Files at Software Informer. Comparison of Gear Calculation Equations....... 1.2 Metric Standards. 5.3 Internal Gear With Small Differences In Numbers Of Teeth....... 6.2 Fundamentals Of Helical Teeth.

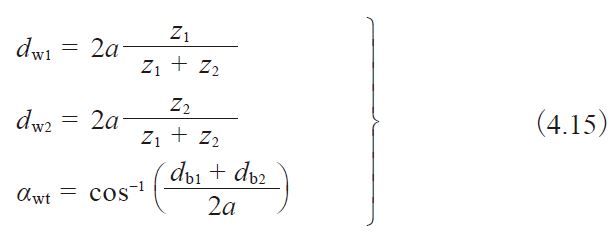
The Boussinesq theory is applied for calculating the local contact deformations. The bending is determined by the combination of only one standard finite element method computation and interpolation functions. This method allows taking into account the environment of the gear meshing, such as the actual shafts, rim, web, bearing locations, which affect the quasi-static results and thus the wear. In addition, the model allows to obtain numerous results, such as load sharing, contact pressures distribution, transmission error, stiffness, wear distribution, etc. A comparison between theoretical wear predictions and experimental results, issued from the literature, are also presented.






